
However, when the switch boots with the IP address 0.0.0.0 configured on both the sc0 and me1 interfaces, the me1 interface is brought down to allow BOOTP and RARP requests to broadcast out the sc0 interface.
#Cisco switch default gateway software
In most cases, the switch software brings down the sc0 interface after you confirm the change. Therefore, when you enter a command that causes sc0 and me1 to have the same IP address or occupy the same subnet, the switch software brings one of the interfaces down. The switch IP routing table is used to forward traffic originating on the switch only, not for forwarding traffic sent by devices that are connected to the switch.īecause sc0 and me1 are two distinct interfaces, they potentially can have duplicate IP addresses or overlapping subnets. For intersubnetwork communication to occur, you must configure at least one default gateway for the sc0 or me1 interface. When you configure the SLIP (sl0) interface, you can open a point-to-point connection to the switch through the console port from a workstation.Īll IP traffic that is generated by the switch (for example, a Telnet session that is opened from the switch to a host) is forwarded according to the entries in the switch IP routing table. When you configure the IP address, subnet mask, and broadcast address (and when you configure VLAN membership on the sc0 interface) of the sc0 or me1 interface, you can access the switch through Telnet or SNMP. The out-of-band management interfaces (me1 and sl0) are not connected to the switching fabric and do not participate in any of these functions.

The in-band (sc0) management interface is connected to the switching fabric and participates in all of the functions of a normal switch port, such as spanning tree, Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), and VLAN membership. The Catalyst 4500 series, the Catalyst 2948G, Catalyst 2948G-GE-TX, and the Catalyst 2980G switches have three management interfaces:

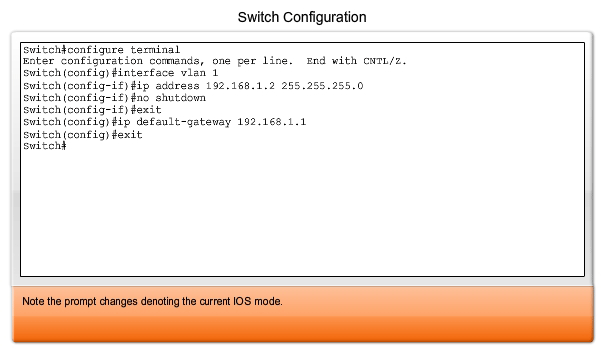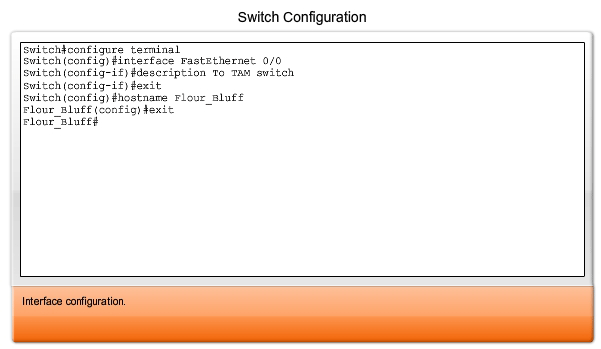
On that switch, now you can configure interface Gi1/0/1 as: switchport mode trunk Plug FastEthernet 0/0 from the Router/Firewall into your Switch, lets say Gi1/0/1:
#Cisco switch default gateway series
Then you configure your first switch, which in a small business is often a 元 capable SB Cisco SG Series or a C1K switch, treated like a "Core". If you have a router/firewall and you are doing 'router on a stick' or have each subnet connected from the router via its own interface to the switch capable of Layer 3 also, then on the switch you can have multiple gateways of last resort.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
